
Scrum is the methodology or framework that we have chosen to work on our projects. In the same way, this implies many things. When we talk about a methodology, we think of a lot of reading and more to do, but really Scrum is more about acting, about doing some specific things that lead to the success of a project through the implementation of the methodology.
It is more difficult to break paradigms or precepts that are held in and for daily work than to implement Scrum, the critical point is to see that it is not really complex and that if you take some actions you can be part of the flow.
What does it mean to be agile?
- Continuously generate value: Not always, but continuously.
- Collaboration: it is important to detect when it is needed and carry out the activities that require it.
- Adaptation: Responding to changing times, but at the moment in which they happen.
- Continuous improvement: Know the points for improvement, identify and correct.
The most important concepts of the Agile methodology will be named below.
SCRUM:
The term comes from the sport of rugby and refers to an agile work methodology that seeks to optimize teamwork through a system of continuous deliveries and reviews that guarantee the achievement of the proposed objectives.
The team?
Scrum master: This is the facilitator who will control all the information and can provide the questions, answers, technology and everything the team needs to complete what was planned in a sprint.
Product Owner:
He is the owner of the product, in many cases he is on the client's side, but he is also on the team's side. Ideally, he should be invited to the methodology and be part of the meetings. As an initial task, he must deliver a Backlog to start working.
Development Team: The idea is to work as a team, where everyone complements each other.
Stakeholders : They are basically all the people who participate in the project but are not part of the Scrum team.
Ceremonies and concepts
- Sprint planning: Planning of each sprint, from Backlog the tasks to be carried out are taken, the user stories are defined and detailed and included in the work to be done in the sprint.
- Daily Scrum: Daily Meetings.
- Sprint: Each Sprint represents a completed deliverable.
- Sprint review: lessons learned – Retrospective.
Team speed
- Pivot: Task that everyone understands and measures – To give value to a point, know each task and how long it would take the team to develop each one.
- The points: Quantification for planning – The idea is to find a unit that can be given value in points and measure the effort accordingly. necessary to perform tasks.
- Teamwork: Frontend, backend, Quality Assurance… and design? what about the design team?
This measurement must be a team effort; since a task requires 10% Quality Assurance, 50% backend and 40% frontend, it does not make the work of the quality assurance (QA) team less important. .
In a task it may happen that the backend time is 10% and a Quality Assurance task is 90%, meaning that the level of importance of each team is the same.
Sprint Review
The result of the review is positive things that we managed to do and can improve, that were done poorly and that can be improved for the next sprint.
The idea is to see and improve.
Paradigms and Solutions
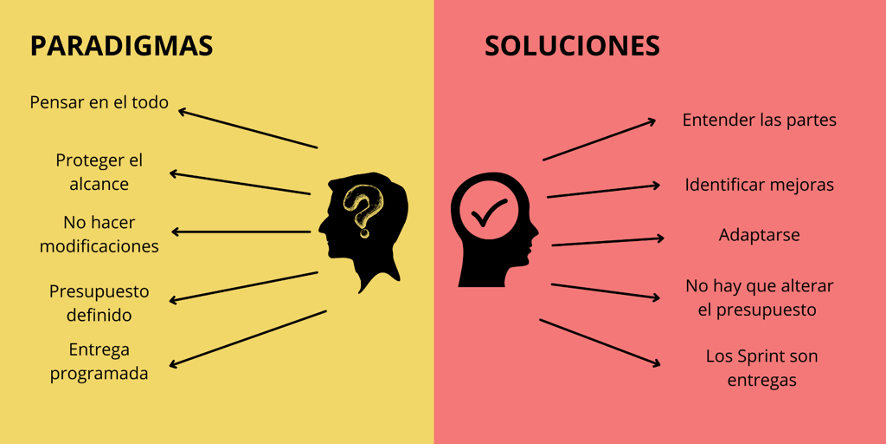
We invite you to think about the parts of the projects and understand them as they are, and not about the whole project, which can change and evolve, and we should not deal with everything until the time comes.
